Patient Normothermia Management's
Thermoregulation is the biological mechanism responsible for maintaining a steady internal body temperature.
Hypothalamus is a section of our brain that controls thermoregulation Hypothalamus helps to manage our Body temperature, Blood Pressure, Hunger and Thirst, Sense of fullness when eating, mood, Sleep.
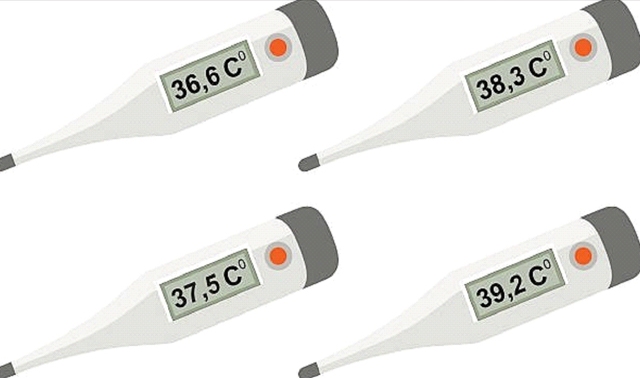
The average person has a baseline temperature between 98°F (37°C) our body has some flexibility with temperature. However, the body temperature above 37 degree centigrade or below 37 degree centigrade temperature can affect your body's ability to function.
The human body maintains a temperature of about 98.6°F (37°C) using various physical processes. These include sweating to lower the body temperature, shivering to raise it if our body temperature falls lower than 35 degree centigrade, We have hypothermia. This condition can lead to cardiac arrest, brain damage, or even death. if our body temperature rises above 104°F (40°C).
Heat stroke is considered a medical emergency. If our body temperature rises to high, we can experience brain damage or even death.
Many factors can affect our body's temperature, such as spending time in cold or hot weather.
Our hypothalamus is a section of your brain that controls thermoregulation. When the hypothalamus senses your internal temperature becoming too low or high, it sends signals to our muscles, organs, glands, and nervous system.
They respond in various ways to help return your temperature to its typical levels.
If our internal temperature drops or rises outside of the typical range, our body will take steps to adjust it. This process is known as thermoregulation.
It can help us to avoid or recover from potentially dangerous conditions like hypothermia or Hyperthermia.
If an individual is unable to regulate their temperature, they could overheat, leading to hyperthermia. If the core temperature falls below a safe level, it will cause hypothermia. Both conditions can potentially be life threatening.
Forced air patient warming system
The patient warming system is a convective temperature management device that maintains a patient's core body temperature in a hospital or operation theater.
Before, during, and after the operation,Forced air warming. Air is sucked in from the surroundings and warmed using electric coils. The blower circulates the warm air through a blanket that warms the patient through convection.
Forced-air warming systems filter air through HEPA & Plasma filters and then force the warm air through a disposable blanket, which cover patients
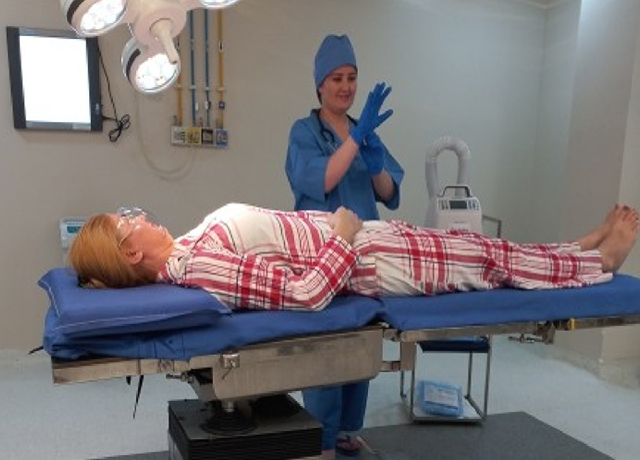
Before Surgery
During Surgery
